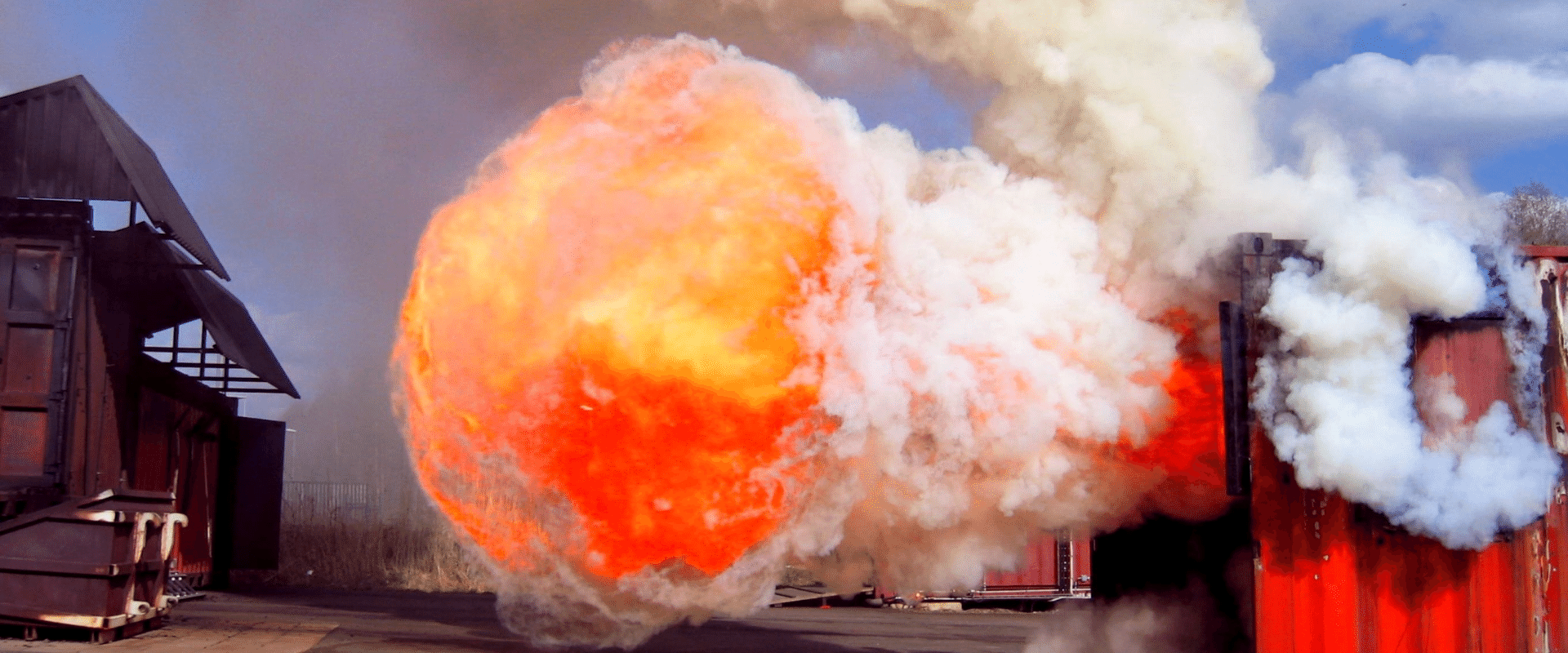
What is DSEAR? DSEAR stands for Dangerous Substances and Explosive Atmosphere Regulations 2002.
DSEAR places duties on employers and the self-employed to protect people in the workplace, and the public, from the risk of fire, explosion and the corrosion of metal caused by their work activity.
Although it may sound like it only affects high risk businesses, it does in fact apply to most workplaces that use things such as solvents, paints, varnishes, dust from machinery or sanding operations, bakeries and other places where flour dust is present, liquid petroleum gases (LPG), pressurised gases and chemicals or substances that are corrosive to metals.
What are employers duties under DSEAR?
Employers have a duty under the DSEAR regulations to establish and control the following.
1) To find out what dangerous substances are in their workplace and what the risks are.
2) To develop and implement control measures to either remove those risks or, where this is not practicable, bring them under control to bring any risk down to the lowest possible level.
3) To develop controls to reduce the effects of any incidents involving dangerous substances.
4) To have plans and procedures in place to deal with accidents, incidents or emergencies that may arise involving dangerous substances.
5) To have suitable training and information to ensure employees are fully conversant on how to control or deal with the risks from a dangerous substance or substances.
6) To identify and have classified areas of the workplace where explosive atmospheres may occur and eliminate sources of ignition in those areas.
What are the regulations?
DSEAR falls under the COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health) regulations.
However, it also falls under the duties of the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations as conducting a risk assessment of the workplace activities is key to controlling and applying safe measures in any situation.
That said, a risk assessment under DSEAR is only necessary if a dangerous substance is, or is liable to be present in the workplace.
The regulation stipulates that the following are considered:
1). What are the hazardous properties of the substance?
2). What information on safety is provided by the supplier. Is there relevant information contained in any safety data sheet?
3). What does the work entail?
4). Other activities, such as cleaning and maintenance, where there is the potential for a high level of risk.
5). The effect of measures which have been or will be taken.
6). The likelihood that an explosive atmosphere will occur and its persistence.
7). The likelihood of ignition sources being present, including electrostatic discharges.
8). The scale of a fire or explosion should one occur.
9). Places which are connected, or have the potential to be connected to other areas where explosive atmospheres may be present or occur.
10). Such additional safety information as the employer may need in order to complete the risk assessment.
Consider the following:
1). The process and substances used in the work, including the possibility of any interaction.
2). How much substance is involved.
3). The risk presented by combining more than one dangerous substance.
4). The arrangements for safe handling, storage and transport of dangerous articles and substances-including waste (as required by the Health & Safety at Work Act 1974- Section 2 and COSHH regulations).
Storage:
Dangerous substances should be kept in a safe place in a separate building or the open air, with only a small quantity of the dangerous substance kept in a work area.
For flammable liquids that have a flash point above the maximum ambient temperature (normally considered to be 32-degrees Celsius), the quantity that may be stored in the work area is an amount up to 250 litres.
For extremely flammable liquids and those with a flash point below the ambient temperature, then the maximum quantity that can be held in a work area is up to 50 litres, and should be held in a purpose built metal container or cupboard.
Similar guidance also applies to the following Flammable Gases, Aerosols and Combustible Materials
For further in depth guidance on DSEAR and other regulations, please visit our ever-increasing Knowledge Base.
And last but not least
We all have a role to play in effective health and safety, and for those actively involved in promoting safe working practices it can be a rewarding, interesting and varied role.
Please visit this site often where you will find a growing number of articles, resources, advice and opinion.
Whether you are a seasoned health and safety professional, or just getting started, we value your opinions and input so please feel free to comment on any of the posts.
Due to the ever-changing nature of regulations and the law, please visit http://www.hse.gov.uk/ for the very latest information and updates.